No products in the cart.
Biotin Binding Surfaces
Applications & TechniquesStreptavidin and Neutravidin offer a powerful and universal instrument as biotin binding surfaces (Antibodies – Antigens – Peptides – Polysaccharides – Oligonucleotides – DNA fragments – etc.) and are suitable to set up different kind of immune-molecular tests.
Biotin is a small molecule (M.W. 244 Da) which can be conjugated to many proteins without losing or altering their activity and each protein can bind many biotin molecules.
Biotin Binding Surfaces Characteristics
Biomat biotin-binding 96-well coated plates include:
- Streptavidin Coated 96-Well Plates
- Streptavidin High Binding Coated 96-Well Plates
- Neutravidin Coated 96-Well Plates
Biomat biotin-binding PCR products include:
- Streptavidin PCR 8 Strip Tubes
- Streptavidin HB PCR 8 Strip Tubes
- Streptavidin PCR Plates
- Streptavidin HB PCR Plates
Streptavidin is a tetrameric protein (M.W. 60 kDa) with very high affinity for biotin (Ka=10-15M); the bond is the strongest known non-covalent biological interaction.
Neutravidin is a deglycosylated avidin (M.W. 60 kDa) that contains four identical subunits biotin-binding with very high affinity for biotin (Ka= 10-15 M). It has an isoelectric point near-neutral (pI=6.3) and the lowest nonspecific binding properties among the known biotin binding proteins. Compared to the streptavidin, neutravidin in its primary structure does not contain the RYD sequence (Arg-Tyr-Asp). The lack of that kind of sequence totally eliminates the possibility to interact with the RGD sequence (Arg-Gly-Asp) present in the membrane receptors of a large variety of cells.
Streptavidin and Neutravidin coated plates offer greater assay’s sensitivity given that each of their four subunits binds one molecule of biotin.
Surfaces:
The streptavidin/neutravidin-biotin bonding main features are:
- stability
- specificity
- affinity
These bonding characteristics are useful for special applications of molecules which do not offer reliable bonding by passive adsorption or adsorb in an unfavorable orientation.
Applications
Which are the applications of biotin-binding surfaces such as Streptavidin and Neutravidin?
- ELISA sandwich assay test: among the different ELISA tests for the dosage of antigens (e.g. TSH) this test offers high sensitivity performance and proper reactivity. However, it requires that one of the two antibodies is bound directly to the microplate (medium or high binding) requiring an antibody coating concentration of at least 3 µg/ml. By using a streptavidin or neutravidin* coated microplate, after the biotinylation of the catcher antibody, it is possible to obtain the same sensitivity and reactivity performance with 0,5 – 1 µg/ml of antibody saving a significant amount of product. Furthermore, the attack of the biotinylated antibody is sterically more favored to react with the antigen and consequently favors the sandwich with the detector antibody.Indirect ELISA test: binding a low molecular weight peptide directly to the microplate is limiting and difficult on medium or high binding microplates. It is more effective and easy to biotinylate the peptide and to bind it to the streptavidin or neutravidin* microplate.
- Competitive ELISA test: in the competitive test the anti-molecule biotinylated antibody, which must be present in a limited concentration, can be bound to the streptavidin or neutravidin* microplate to guarantee the correct competition between the dosed molecule and the analogous enzyme labeled molecule.
- PCR-ELISA test: streptavidin or neutravidin* microplate may be used to set up a PCR-ELISA test, taking advantage of the high specificity and stability established in the binding of biotinylated oligonucleotide during the hybridization step.
*Neutravidin coated surfaces are suitable for the same type of applications offering a lower background.
Biomat biotin-binding characteristics:
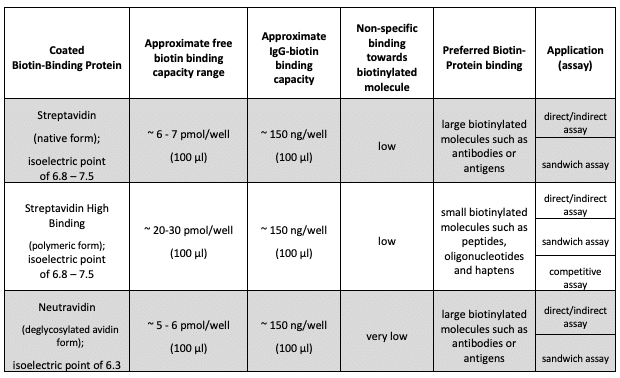
Biotin Binding Surfaces Tests
Below we have reported our tests of the binding capacity for biotinylated human IgG and free biotin comparing Streptavidin, Streptavidin High Binding and Neutravidin coated surfaces.
Binding capacity towards biotinylated human IgG
Method
Streptavidin, Streptavidin High Binding and Neutravidin coated wells were incubated with 100 µl solutions (from 0 to 2.5 µg/ml) of biotinylated human IgG for 30 minutes at room temperature.
After a washing step, the wells were incubated with goat anti human IgG-peroxidase for 30 minutes at room temperature, again washed and incubated with TMB for 10 minutes at room temperature and blocked with sulphuric acid 1N.
The mO.D. values were read at 450 nm.
Results
The comparison among Streptavidin, Streptavidin High Binding and Neutravidin coated surfaces to bind large molecules does not show differences in term of bound IgG.
The figure below shows that a plateau of biotinylated human IgG has got starting from 1.5 µg/ml (150 ng/well) for all three kind of plates.

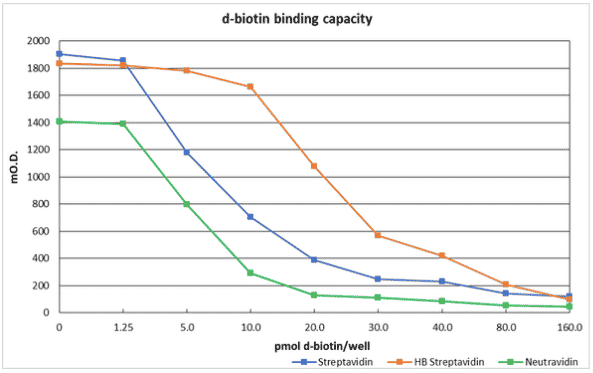
Binding capacity towards free biotin
Method
Streptavidin, Streptavidin High Binding and Neutravidin coated wells were incubated with 100 µl biotin solutions (from 0 to 1,600 pmol/ml) containing 1.3 ng/ml of biotinylated peroxidase for 30 minutes at room temperature.
After a washing step, the wells were incubated with TMB for 15 minutes at room temperature and blocked with sulphuric acid 1N.
The mO.D. values were read at 450 nm.
Results
The comparison between Streptavidin, Streptavidin High Binding and Neutravidin coated surfaces to bind a small molecule shows a significant difference in terms of the biotin bound on the surface.
The figure below shows that the Streptavidin High Binding plate has a binding capacity of about 21.1 pmol/well while Streptavidin is about 6.8 pmol/well and for Neutravidin plate is about 5.7 pmol/well.
The Streptavidin High Binding coated surface is more suitable to set up ELISA competitive assay for the dosage of small molecules.
Calculation of binding capacity
The binding capacity of biotin expressed as pmol/well has been calculated with the IC50 measuring.
The half maximal inhibitory concentration (IC50) is a measure of the potency of a substance in inhibiting a specific biological or biochemical function. IC50 is a quantitative measure that indicates how much of a particular inhibitory substance (e.g. biotin in our test) is needed to inhibit, in vitro, a given biological process or biological component by 50%. The biological component could be an enzyme, cell, cell receptor or microorganism. IC50 values are typically expressed as molar concentration.
The IC50 of biotin has been determined by constructing a dose-response curve and examining the effect of different concentrations of biotin (antagonist) on reversing (agonist) biotin-peroxidase activity. IC50 values have been calculated for biotin by determining the concentration needed to inhibit half of the maximum biological response of the biotin-peroxidase.
Here Biomat biotin binding products:
Biotin-binding 96-well coated plates
- Streptavidin Coated 96-Well Plates
- Streptavidin High Binding Coated 96-Well Plates
- Neutravidin Coated 96-Well Plates
Biotin-binding PCR products
- Streptavidin PCR 8 Strip Tubes
- Streptavidin HB PCR 8 Strip Tubes
- Streptavidin PCR Plates
- Streptavidin HB PCR Plates
Additionally, Biomat offers Biotin Coated Plates that are ideal as the basis for a variety of immunoassays techniques requiring the immobilization of probes that are conjugated with biotin-binding proteins.
Biomat Biotin Coated Plates





